
Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia)
Also known as: Grape-Woodbine, Five-leaved ivy, Woodbine
The Virginia Creeper, a North American vine from the grape family, boasts robust growth, fragrant blooms, and striking blue berries. Its leaves transform to a vivid crimson in autumn. Equipped with small forked tendrils and adhesive pads, it firmly attaches to various surfaces, often covering entire walls and offering habitat and nourishment for wildlife.
Attributes of Virginia creeper
Images of Virginia creeper

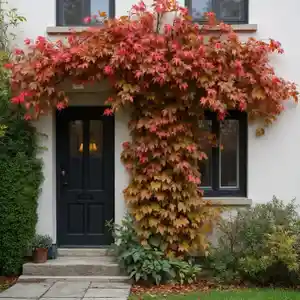


Quickly Identify Virginia creeper
Scientific Classification of Virginia creeper
Planting and Growing of Virginia creeper
 How to Water Virginia creeper?
How to Water Virginia creeper?
 What Are the Sunlight Requirements for Virginia creeper?
What Are the Sunlight Requirements for Virginia creeper?
 What Is the Ideal Temperature Range for Virginia creeper?
What Is the Ideal Temperature Range for Virginia creeper?
 What Soil is Best for Virginia creeper?
What Soil is Best for Virginia creeper?
 How to Fertilize Virginia creeper?
How to Fertilize Virginia creeper?
 How to Prune Virginia creeper?
How to Prune Virginia creeper?
 How to Propagate Virginia creeper plant?
How to Propagate Virginia creeper plant?
 How to Repot Virginia creeper plant?
How to Repot Virginia creeper plant?
Toxicity of Virginia creeper
Is Virginia creeper toxic to humans?
The berries of the Virginia creeper are laden with dangerously high concentrations of oxalic acid, which can be lethal to humans if consumed. Additionally, ingesting these berries may lead to kidney damage. Symptoms of poisoning from Virginia creeper may manifest as nausea, vomiting, or dizziness. Furthermore, the sap found in the leaves and stem can cause skin irritation in certain individuals. Given its rapid growth as a vine that can either ascend structures or spread along the ground, people might unintentionally encounter fractured sections of the plant and become exposed to its sap.
Is Virginia creeper toxic to cat?
Virginia creeper can be mildly toxic to cats, presenting potential risks if ingested in large quantities. Every part of the virginia creeper plant carries the ability to be harmful. If consumed, a cat may exhibit signs of physical distress, suggesting possible poisoning. It is crucial for cat owners to monitor their pets' interactions with this plant. In cases of ingestion, swift consultation with a veterinary clinic is essential for effective treatment, safeguarding the health and well-being of the feline friend.
Is Virginia creeper toxic to dog?
Virginia creeper presents a mild toxicity risk to dogs. Canines are at risk of poisoning from this plant if they ingest it in large quantities. Every part of the virginia creeper plant is deemed toxic and can lead to negative reactions in dogs. Should a dog chew or consume any portion of virginia creeper, it may display symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or excessive drooling. It's essential for dog owners to keep a close eye on their pets and restrict their access to areas where virginia creeper is present. If a dog does consume virginia creeper, it is crucial to seek prompt veterinary assistance to ensure the best possible outcome for the animal.














