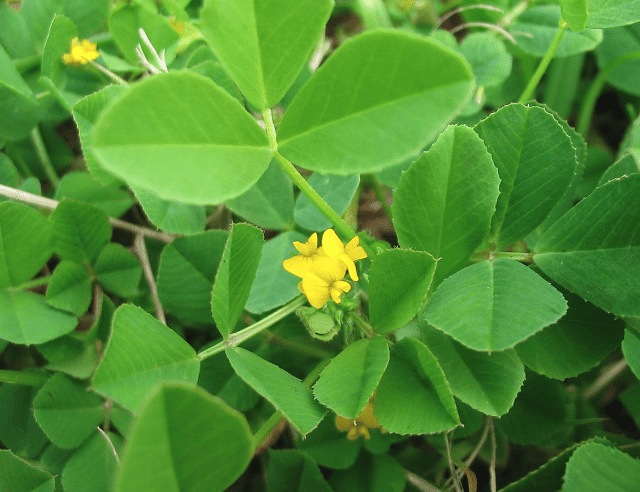
Bur clover (Medicago polymorpha)
Bur clover, also known as Toothed medick, Toothed bur clover, California burclover, Bur medick
Bur clover, also known as Medicago polymorpha, burr medic, or creeping burr, offers several agricultural benefits. As a legume, it enriches the soil by fixing atmospheric nitrogen, thereby reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. It also improves soil structure and boosts organic matter, which enhances water retention and aeration, making it an excellent green mulch. Additionally, bur clover serves as nutritious forage for livestock, especially sheep, and can act as emergency forage if other crops fail. It also helps control soil erosion with its dense growth.
However, bur clover comes with its risks. It has the potential to become invasive, outcompeting other crops and native plants. Its burrs can stick to animals and machinery, leading to unintended spread and infestation. There is also the risk of allelopathy, where it may release chemicals that inhibit the growth of other plants, potentially affecting crop yields. Lastly, the burrs can cause discomfort or injury to livestock if they get stuck in their fur or are ingested. Balancing these benefits and risks is crucial for effective agricultural management.