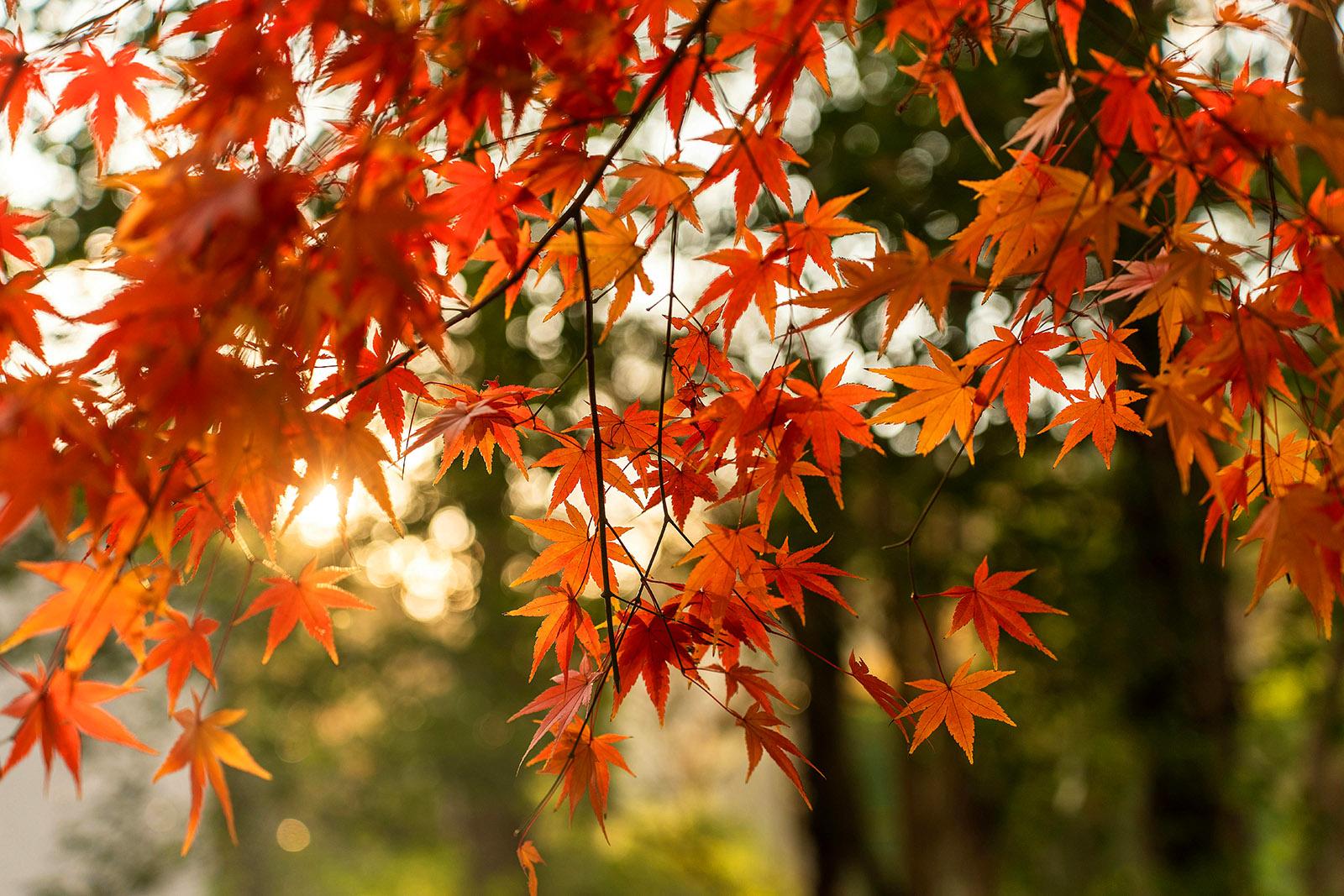
Maple trees (Acer species) are among the most popular landscape trees in North America, valued for their stunning fall colors, shade provision, and architectural beauty. With over 130 species worldwide, these deciduous trees offer incredible diversity for every garden size and climate zone. This expert guide covers 15 exceptional maple varieties perfect for residential landscapes.
Key Points
- Spectacular fall colors ranging from fiery reds to golden yellows
- Perfect for shade, street planting, and specimen trees
- Wide climate adaptability from USDA zones 2-9
- Generally drought-tolerant once established
- Sizes from compact 15-foot varieties to majestic 100-foot giants

Why Choose Maple Trees for Your Landscape
According to USDA research, maple trees provide exceptional ecological benefits including carbon sequestration, wildlife habitat, and urban heat reduction. Their dense canopy offers superior shade coverage, while their vibrant autumn display creates lasting visual impact.
'Maple trees are the workhorses of urban forestry. They combine beauty with functionality, providing shade in summer and spectacular color in fall while requiring relatively low maintenance.' - Dr. Michael Roberts, Urban Forestry Expert
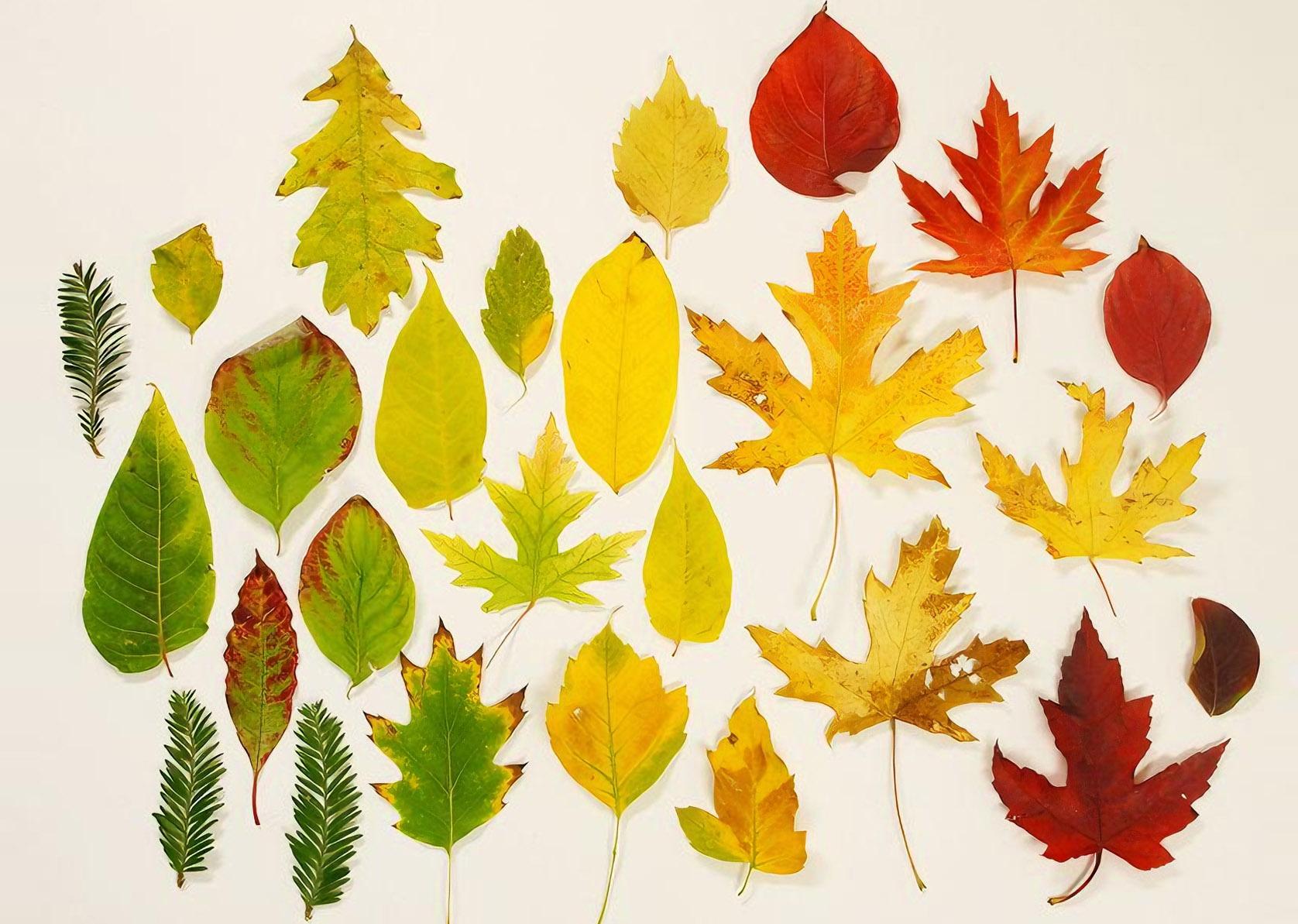

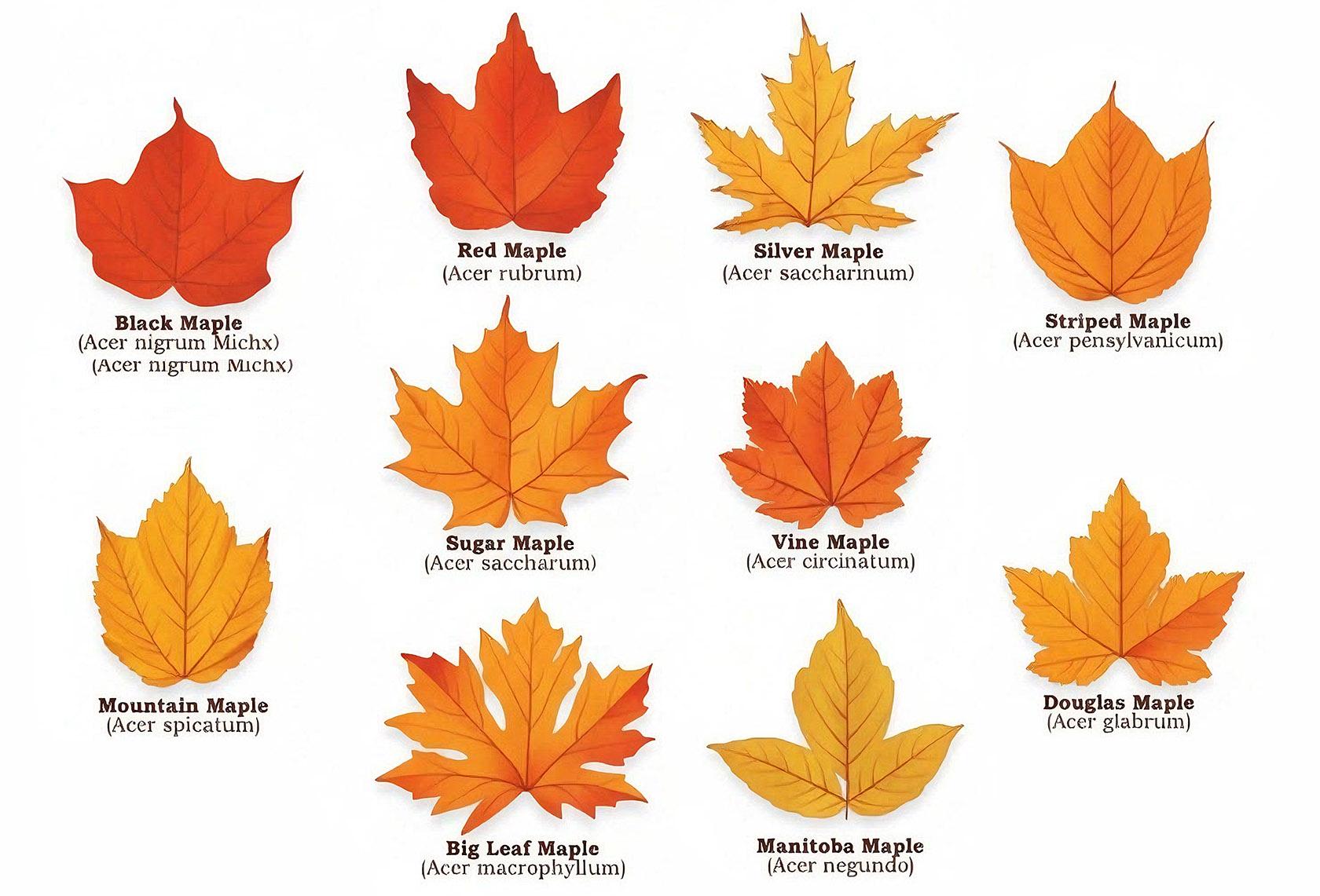
How to Identify Maple Trees
- Leaves: Classic palm-shaped with 3-9 lobes (varies by species)
- Seeds: Winged samaras that spin like helicopters when falling
- Bark: Smooth when young, developing furrows with age
- Flowers: Small, inconspicuous clusters in spring
- Fall Color: Ranges from yellow to orange to brilliant red
Pro Tip: Use PlantJoy's tree identification feature to instantly identify maple species and get customized care recommendations based on your specific tree and local climate conditions.
Best Maple Trees for Different Landscape Needs
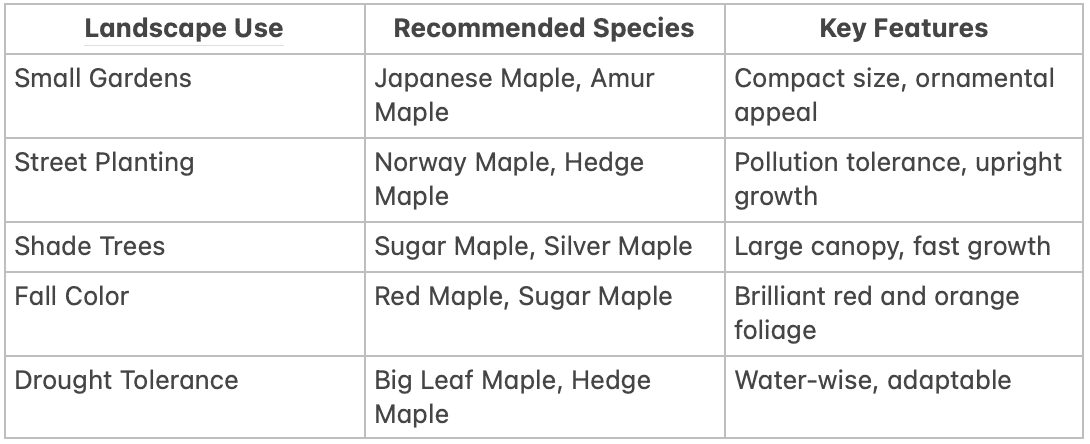
Top 15 Maple Tree Species Detailed Guide
1. Amur Maple (Acer ginnala) - Compact Beauty
- Native Area: Korea, Japan, Mongolia, Siberia
- USDA Zones: 3-8
- Height: 15-20 feet
- Sun: Full sun to partial shade
- Fall Color: Vibrant red with yellow accents
Perfect for small landscapes, the Amur maple works beautifully as a multi-stem shrub or small tree. Its 'Embers' and 'Flame' cultivars offer exceptional fall color. Excellent winter hardiness and some drought resistance once established.
2. Big Leaf Maple (Acer macrophyllum) - Majestic Giant
- Native Area: Western North America
- USDA Zones: 6-7
- Height: 50-100 feet
- Sun: Full sun to full shade
- Fall Color: Golden yellow
As the name suggests, this species features the largest leaves of any maple (up to 12 inches wide). Perfect for large landscapes and parks, providing massive shade coverage. Spring foliage emerges burgundy, turning green in summer.
3. Hedge Maple (Acer campestre) - Urban Champion
- Native Area: Europe, Southwestern Asia
- USDA Zones: 5-8
- Height: 25-35 feet
- Sun: Full sun to part shade
- Fall Color: Yellow
Exceptionally tolerant of urban conditions including drought, pollution, and compacted soils. Can be pruned as a hedge or grown as a small shade tree. Excellent winter hardiness.
4. Japanese Maple (Acer palmatum) - Ornamental Masterpiece
- Native Area: China, Korea, Japan
- USDA Zones: 5-9
- Height: 15-25 feet
- Sun: Partial shade preferred
- Fall Color: Red, purple, bronze
With thousands of cultivars available, Japanese maples offer incredible variety in leaf shape, color, and texture. Perfect as focal points in garden designs. Dwarf varieties work well in containers and small spaces.
5. Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum) - Autumn Legend
- Native Area: Northeastern US, Canada
- USDA Zones: 3-8
- Height: 50-80 feet
- Sun: Full sun to full shade
- Fall Color: Brilliant orange-yellow
Famous for maple syrup production and spectacular fall color. Prefers well-drained soil and doesn't tolerate urban pollution well. Excellent shade tree for large properties with good winter hardiness.

Expert Planting and Care Guide
- Choose the right species for your climate zone and space requirements
- Plant in well-drained soil with proper spacing for mature size
- Water deeply during establishment (first 2-3 years)
- Apply mulch around base to retain moisture and regulate temperature
- Prune during dormancy to maintain shape and remove dead wood
- Monitor for common pests like aphids and scale insects
Based on my 20 years of arborist experience, proper planting technique is crucial for maple tree success. Always plant at the same depth as the nursery container and avoid planting too deep, which can lead to root rot.
Watering and Fertilization Tips
Maple trees generally prefer consistent moisture but become drought-tolerant once established. Use PlantJoy's smart watering reminders to receive personalized irrigation schedules based on your tree species, soil type, and local weather conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. When is the best time to plant maple trees?
Early spring or fall, when temperatures are moderate and rainfall is more consistent. Avoid planting during summer heat or winter freeze periods.
2. How fast do maple trees grow?
Growth rates vary by species. Silver maples grow quickly (3-5 feet per year), while sugar maples grow moderately (1-2 feet per year). Japanese maples are slower growers.
3. Are maple trees good for urban environments?
Many species like hedge maple and Norway maple tolerate urban conditions well. Avoid sugar maple in polluted areas as it's more sensitive.
4. Can I tap my maple tree for syrup?
Only sugar maple, black maple, and red maple produce sap with sufficient sugar content for syrup production. Trees should be at least 10-12 inches in diameter before tapping.

Climate Considerations by Region
Different maple species thrive in specific climate conditions. Northern regions (zones 3-5) do well with sugar maple and paperbark maple, while southern areas (zones 7-9) prefer red maple and trident maple. Always check your USDA hardiness zone before selecting.
Pest and Disease Management
- Aphids: Use horticultural oil or introduce beneficial insects
- Scale insects: Apply dormant oil spray in late winter
- Verticillium wilt: Choose resistant varieties and ensure good drainage
- Tar spot: Rake and dispose of fallen leaves to reduce fungal spores
PlantJoy's disease diagnosis feature can help identify common maple tree issues and provide targeted treatment recommendations based on expert arborist knowledge.
Seasonal Care Calendar
- Spring: Pruning, fertilization, pest monitoring
- Summer: Deep watering during drought, mulch refresh
- Fall: Leaf cleanup, final watering before freeze
- Winter: Protection for young trees, planning for spring
For personalized care reminders throughout the year, set up PlantJoy's seasonal tree care calendar that sends notifications based on your specific tree species and local climate patterns.

Pro Landscape Design Tips
When designing with maple trees, consider their mature size, fall color timing, and growth habits. Mix different species to extend the autumn color display throughout the season. Use smaller varieties like Japanese maple for focal points and larger species for background planting.
Last updated: October 29, 2024 - Always consult local extension services for region-specific advice






