Bacterial Leaf Spot: Identifying Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments for Your Garden
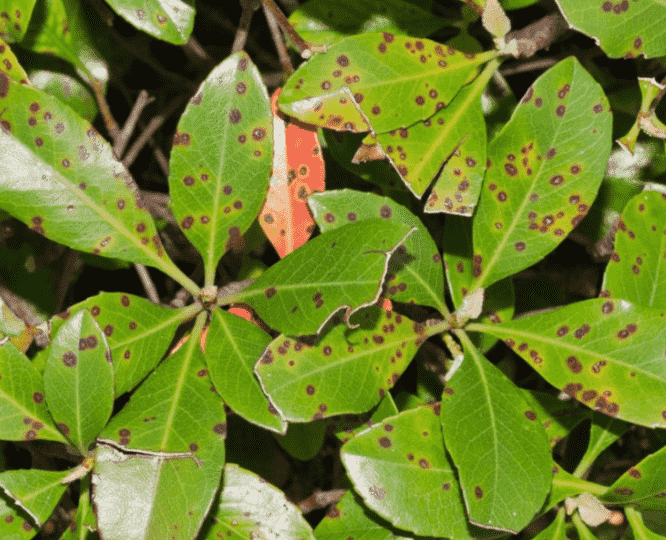
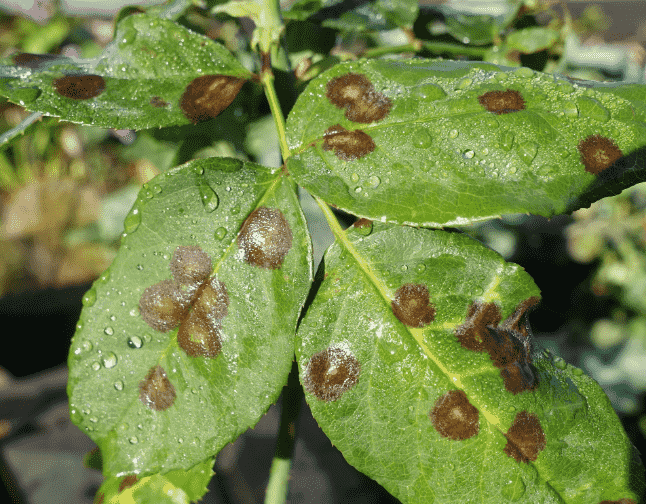
Bacterial Leaf Spot causes small, water-soaked, dark spots on leaves that often develop yellow halos and may merge into larger necrotic areas, leading to premature leaf drop, reduced photosynthesis, defoliation, and decreased overall plant vigor and market quality.
Read More